Calcium ion concentration is determined by measuring the chromogenic complex formed between calcium ions and o-cresolphthalein. The concentration of o-cresolphthalein is proportional to the concentration of calcium ions, and the linear range of detection is 0.4 to 2.0 mg. In this article, the calcium assay method will be looked at in detail.
O-Cresolpht-halein complexon is the colorimetric indicator of choice in the art
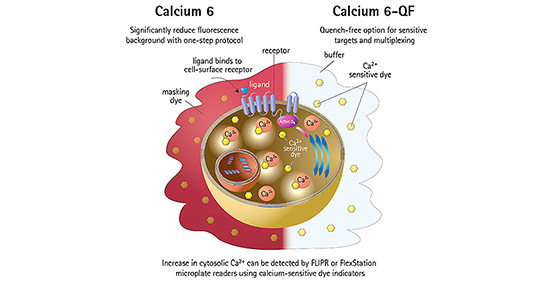
Using synthetic fluorescent Ca(2+) indicators allows scientists to investigate calcium dynamics within cells. TED (targeted-esterase-induced dye loading) is one method that has been widely used in neuronal cultures and cell lines. It is based on efficient targeting of high carboxylesterase activity to the ER lumen. It uses a vector consisting of a core element of CES2 fused to a red fluorescent protein.
This colourimetric indicator is a phthalein dye that is soluble in ethanol and water but insoluble in aqueous solutions. At pH 8.2, o-Cresolpht-halein solution is colourless, while it turns purple when it reaches pH 9.8. It is used in the calcium assay art to determine calcium concentration.
It is based on a novel chromogenic tetracarboxylic acid chelating agent
Calcium concentration is one of the most important parameters to determine the diagnosis of bone disease. Hypercalcemia is a sign of neoplastic bone disease and is associated with numerous malignancies of the bone, including breast, prostate, and kidney cancer. Hypocalcemia is a result of certain medical conditions, including certain medications.
This method uses a chromogenic tetracar plexylic acid chelating agent called Cresolphthalein to measure serum calcium levels. The agent changes colour in response to calcium concentration. The resulting colour represents total calcium levels. The method also detects the presence of free calcium, which is more abundant in nose sweat than in blood.
It forms an immediate colour complex with both ionized and proteinbound calcium
O-Cresolphthalein is an indicator of calcium in biological systems. Its absorption peak is at 575 nm, and its intensity is proportional to the calcium concentration. As calcium is a vital element in biological systems, it is important to measure the concentration of calcium in samples.
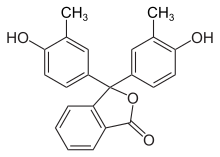
The o-cresolphthalein complexon is the colourimetric indicator of choice for clinical calcium measurements. O-Cresolphthalein has been proven to form an immediate colour complex with both proteinbound and ionized calcium. The o-cresolphthalein complex is colourless below pH 8.2, and purple above pH 9.8. In addition, the compound is used in the production of polyamides.
It requires amphiprotic buffers
The Calcium Assay O-Cresolphthalen Chromogenic Method is a chromogenic assay that uses amphiprotic buffers to determine calcium concentration in biological fluids. The reagents required for this assay are water, amphiprotic buffers with a pH range of 8 to 13, and o-cresolphthalein complex. The reagents are pH-sensitive, allowing for accurate measurements of calcium levels.
TRIS buffer is a specialized solution that contains a tris-sucrose-based medium. It is a buffer system that is commonly used for extracellular invertase production.
It has low on-system stability
A single-reagent colourimetric calcium assay based on a novel chromogenic tetracarboxylic acid chelating agent has several advantages over the o-cresolphthalein complexone method. For example, it is much more robust, has a lower pH of 9.0 (compared with 20.0) and has a linear calibration curve up to 4 mmol/L. A chromatographic study performed on 47 human serum samples showed that the method correlated well with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer and that the mean (+/-SD) calcium values were 2.26 +/-0.05 mmol/L.
This method is particularly suitable for calcium assays in cell cultures. It offers a wide range of measurement options and ultra-fast data sampling. It features a high-precision bottom-reading optical system and supports multiple measurement modes. The instrument also features a temperature-controlled incubator, multiple shaking modes, and reagent injectors.